Oct . 21, 2024 12:34 Back to list
Effective Techniques for Custom Hydraulic Cylinder Bleeding and Maintenance Solutions
Understanding Custom Hydraulic Cylinder Bleeding
Hydraulic systems are critical components in various industrial, automotive, and agricultural applications. They utilize fluid pressure to produce motion, and one of the essential parts of maintaining these systems is proper bleeding of hydraulic cylinders. This process ensures that air is removed from the hydraulic lines, allowing the system to operate efficiently. When it comes to custom hydraulic cylinders, understanding the bleeding process becomes even more crucial.
What is Bleeding in Hydraulic Systems?
Bleeding refers to the process of removing air from the hydraulic fluid in a system. Air trapped in the hydraulic lines can lead to a series of problems, including reduced efficiency, jerky movements, and even damage to the hydraulic components. In a custom hydraulic cylinder, where specifications may differ significantly from standard models, proper bleeding becomes essential to ensure optimal performance.
Why Custom Hydraulic Cylinders?
Custom hydraulic cylinders are designed to meet specific requirements that off-the-shelf products might not satisfy. They can be tailored for different sizes, pressures, and materials based on the application in question. Given their specialized nature, the bleeding process may also require unique considerations. Often, custom cylinders are used in systems that operate under extreme conditions or demand high precision, making proper maintenance, including bleeding, vital.
Steps in Bleeding Custom Hydraulic Cylinders
1. Preparation Before beginning the bleeding process, ensure that the hydraulic system is off, and all safety protocols are followed. Gather all necessary tools, including a bleeder valve wrench and a container to catch any fluid.
custom hydraulic cylinder bleeding
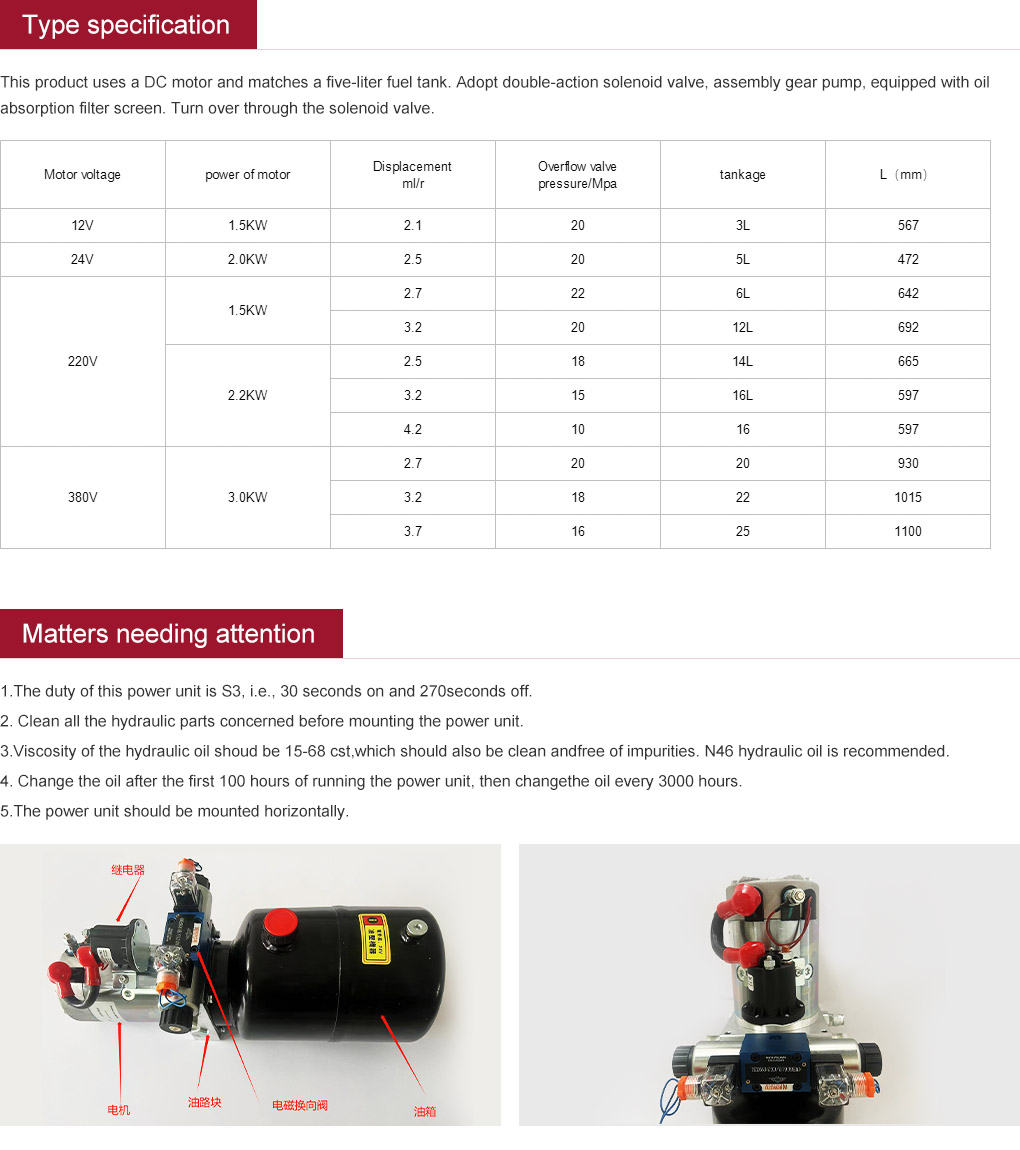
2. Check Fluid Levels Before bleeding, confirm that the hydraulic reservoir is filled to the correct level. Insufficient fluid can complicate the bleeding process and may lead to further air entrapment.
3. Open the Bleeder Valve Identify the bleeder valve on the custom cylinder – this might be located at the end or side of the cylinder, depending on its design. Carefully open this valve to allow air to escape. It is crucial to do this slowly to avoid introducing more air into the system.
4. Actuate the Cylinder While the bleeder valve is open, actuate the hydraulic cylinder. This action helps to push out any trapped air. Depending on the design of the cylinder, extending and retracting the cylinder a few times may be necessary to ensure that all air bubbles are expelled.
5. Close the Valve Once you see a steady stream of hydraulic fluid without air bubbles, close the bleeder valve securely. This step is essential to maintain system pressure and prevent fluid leakage.
6. Re-check Fluid Levels After bleeding, check the hydraulic fluid levels once again. If necessary, top off the reservoir to ensure it remains at the correct level.
7. Test the System With the bleeding process complete, conduct a test run of the hydraulic system. Observe its operation to ensure it is functioning smoothly and efficiently. Any persistent issues may indicate further air presence or other mechanical problems.
Conclusion
Properly bleeding custom hydraulic cylinders is a crucial maintenance task that ensures the efficient and reliable operation of hydraulic systems. By understanding the process and following systematic steps, operators can effectively remove air from their hydraulic components, ultimately enhancing performance and preventing damage. In industries where hydraulic systems play a pivotal role, this knowledge is invaluable, supporting productivity and safety in operations. Regular maintenance, including routine bleeding, should be integral to any hydraulic system management plan, especially for custom-designed equipment.
-
Fork Lift Power Units - Hebei Shenghan | Efficiency, Reliability
NewsJul.13,2025
-
1.5-Ton Turbocharged Cylinder-Hebei Shenghan|Hydraulic Solution,Energy Efficiency
NewsJul.13,2025
-
Auto Hoist Power Units-Hebei Shenghan|Efficiency&Industrial Lifting
NewsJul.13,2025
-
Double Acting Power Units-Hebei Shenghan|Hydraulic Solutions,Industrial Efficiency
NewsJul.13,2025
-
1.5 Ton Lifting Cylinder 70/82-40-290-535 - High-Performance Hydraulic Solution | Hebei Shenghan
NewsJul.13,2025
-
Fork Lift Power Units - Hebei Shenghan | Efficiency&Reliability
NewsJul.13,2025
