ធ្នូ . 23, 2024 00:48 Back to list
Hydraulic Cylinder and Piston Solutions for Efficient Fluid Power Systems
Understanding Hydraulic Pistons and Cylinders Key Components in Fluid Power Systems
Hydraulic pistons and cylinders are fundamental components in fluid power systems, widely utilized in various industrial applications, from manufacturing machinery to automotive systems. These components function together to create mechanical force and motion through the use of pressurized fluid, showcasing the power of hydraulics in modern engineering.
The Basics of Hydraulic Systems
At its core, a hydraulic system operates on the principles of fluid mechanics. It uses liquid—often oil—under pressure to transmit force. The system primarily consists of a fluid reservoir, pump, valves, hydraulic cylinders, and hydraulic actuators. The pump generates fluid flow, and the pressurized fluid is directed through valves to the hydraulic cylinders, where the pistons convert the fluid's energy into mechanical work.
Components of a Hydraulic Cylinder
1. Cylinder Barrel The cylinder barrel is a cylindrical housing that contains the piston. It is designed to withstand high fluid pressure and is often made from durable materials such as steel or aluminum.
2. Piston The piston is a critical component that moves within the cylinder barrel. As pressurized fluid enters the cylinder, it pushes against the piston, generating linear motion. The piston often has seals that ensure fluid does not leak and that maximum force is transmitted efficiently.
3. End Caps The end caps seal the cylinder barrel and keep the piston and fluid contained. They allow fluid to flow in and out of the cylinder while maintaining pressure.
4. Rod The piston rod is attached to the piston and extends out of the cylinder. The movement of the piston is transferred to the rod, which can be connected to machinery or other components to carry out work.
5. Seals and Bearings Seals prevent fluid leakage and maintain pressure, while bearings reduce friction between moving parts, enhancing efficiency and longevity.
The Working Principle
hydraulic piston and cylinder product
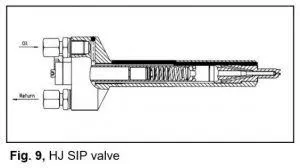
When the hydraulic system is activated, the pump draws fluid from the reservoir and pressurizes it. The pressurized fluid is then directed into the cylinder through control valves. As the fluid enters the cylinder, it exerts force on the piston, driving it forward or backward, depending on the system's design. This movement can be used to lift heavy loads, press materials, or move machinery parts, demonstrating the versatility of hydraulic systems.
The force generated by a hydraulic cylinder is determined by the pressure of the fluid and the area of the piston. According to Pascal's principle, pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished in every direction. This means that even a small piston can generate significant force if the pressure is high enough, making hydraulic systems powerful and effective for heavy-duty applications.
Applications of Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders are used across a vast range of industries, including
- Construction Heavy machinery such as excavators and bulldozers rely on hydraulic systems for lifting and moving heavy materials.
- Manufacturing Hydraulic presses, which utilize cylinders, are essential in forming, shaping, and assembling various materials.
- Automotive Hydraulic brake systems in vehicles use cylinders to control braking power effectively.
- Aerospace Aircraft utilize hydraulic systems for controlling landing gear and wing flaps, showcasing the critical role of hydraulics in safety and performance.
Maintenance and Considerations
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of hydraulic pistons and cylinders, regular maintenance is crucial. This includes checking for leaks, ensuring seals are intact, and monitoring fluid levels and pressure. Contaminated fluid can cause significant damage to the system, making it essential to use clean fluid and replace it as necessary.
In conclusion, hydraulic pistons and cylinders are indispensable components of fluid power systems, enabling the effective transmission of force and motion in various applications. Understanding their design, operation, and maintenance is essential for anyone involved in industries that rely on hydraulic systems. By leveraging the power of hydraulics, businesses can improve efficiency, productivity, and safety in their operations.
-
Premium Set of 50/60-45-290 471 Parts | High Performance
NewsAug.24,2025
-
Efficient & Reliable Double Acting Power Unit | Hydraulic Solutions
NewsAug.23,2025
-
1.5 Ton Turbocharged Cylinder 80/95-40/60-35-124 | High Performance
NewsAug.22,2025
-
High-Performance Fork Lift Hydraulic Power Units
NewsAug.21,2025
-
High-Quality Set of 50/60-45-290 471 - Precision Parts
NewsAug.19,2025
-
1.5 Ton Lifting Cylinder-Hebei Shenghan|Heavy-Duty Lifting, Precision Engineering
NewsAug.18,2025
